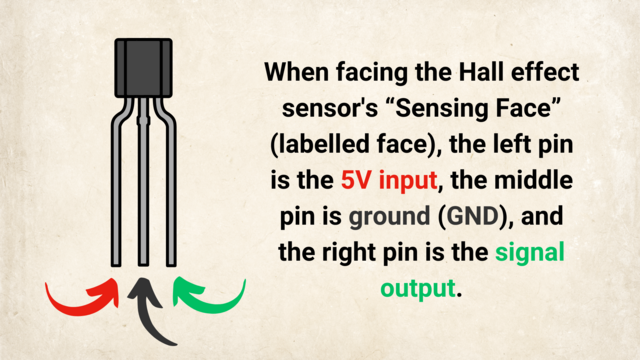
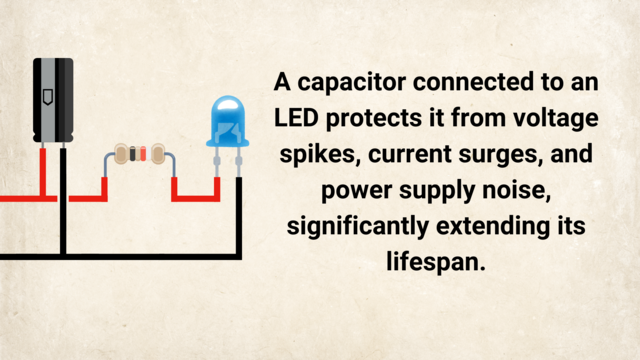
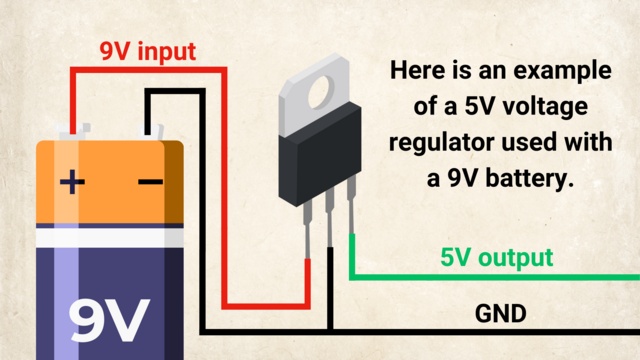
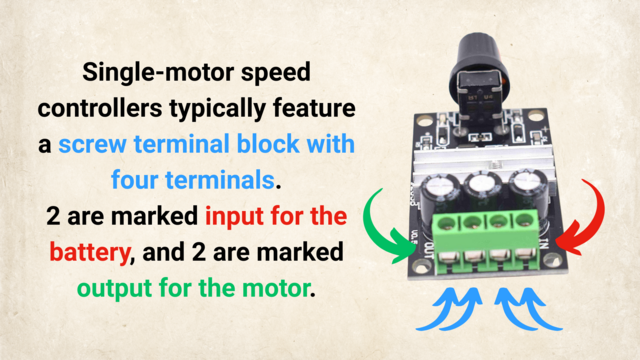
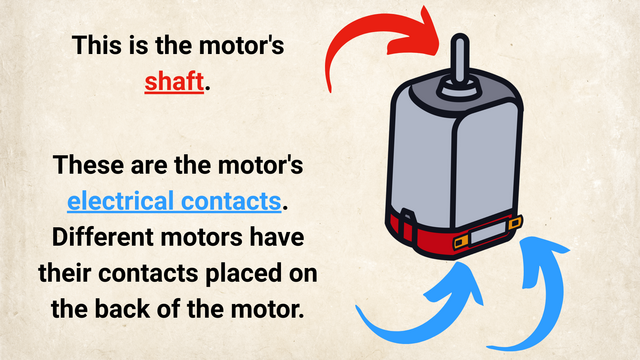
Teacher's Notes: Musical Introduction
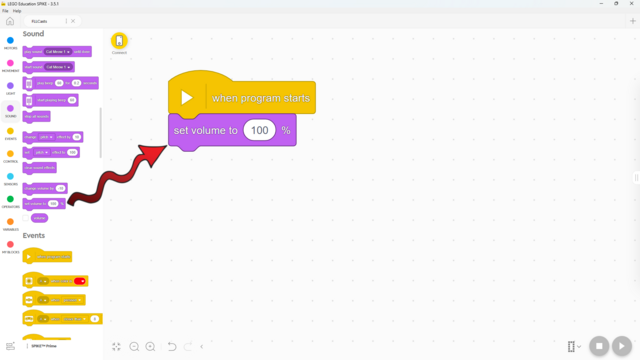
Because this is the musical level, it’s important to set some rules for the sounds the robots make. Students often don’t realize how loud it can get, so remind them to keep the volume lower so they can hear the hubs, and to stop their programs in time, since continuous sounds can become quite loud.
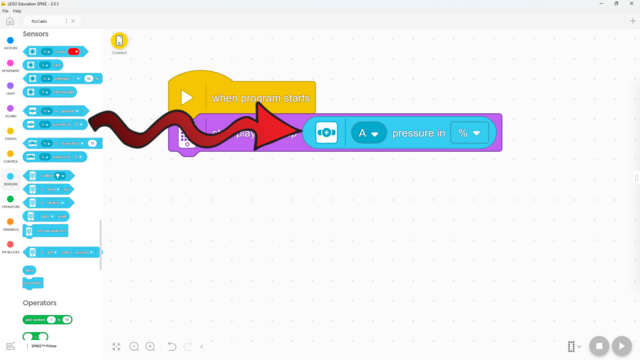
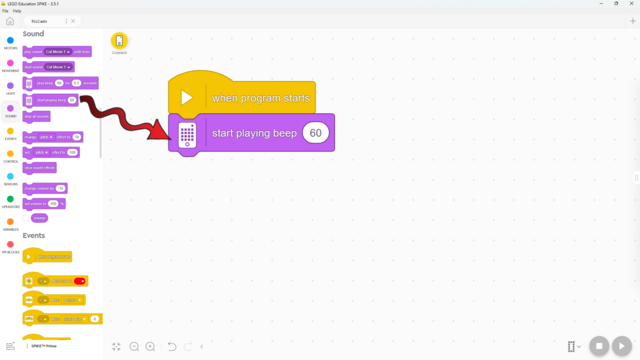
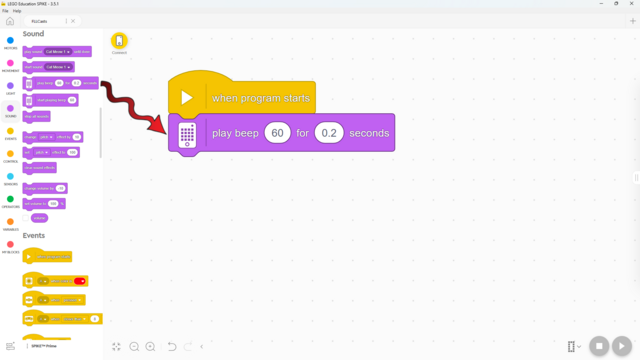
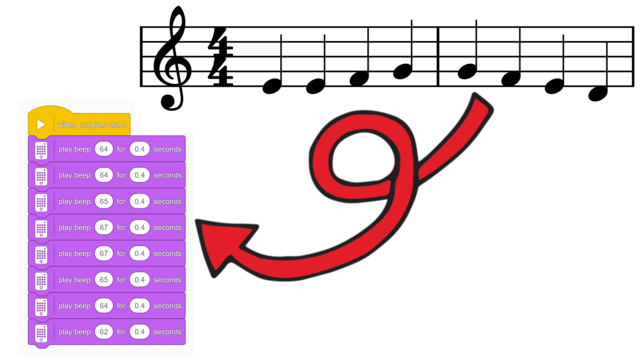
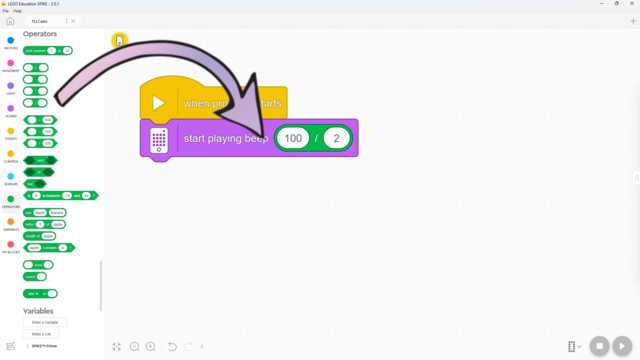
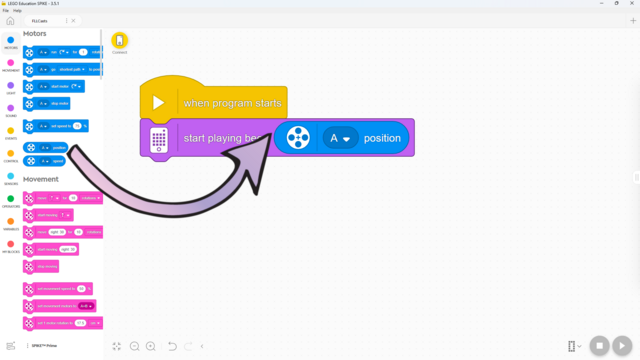
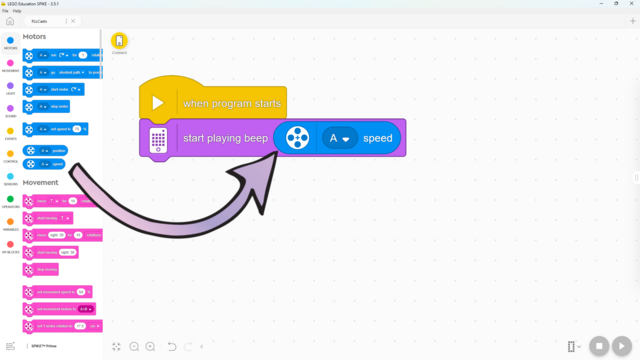
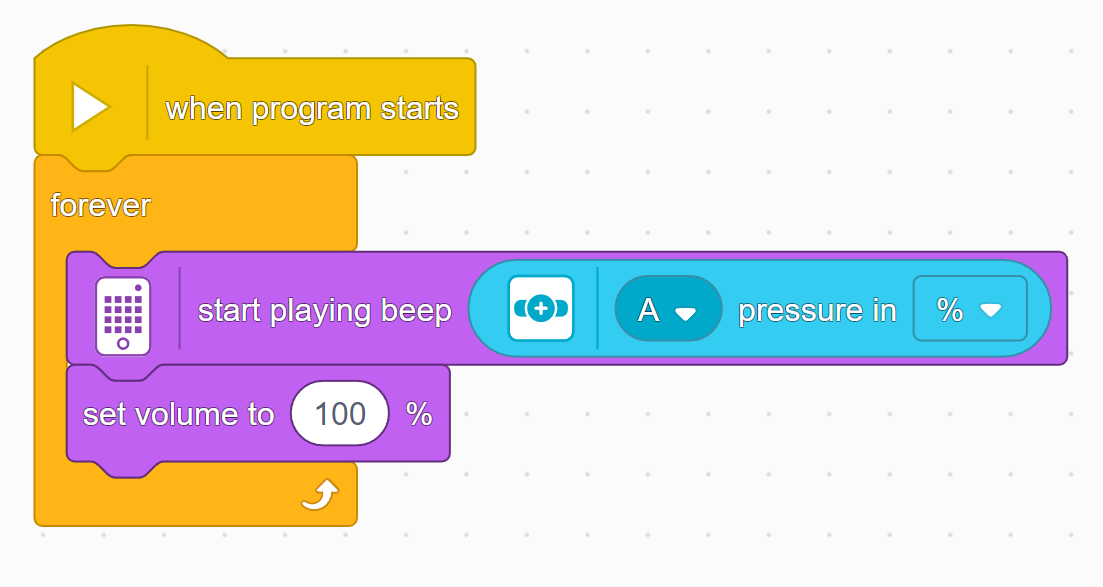
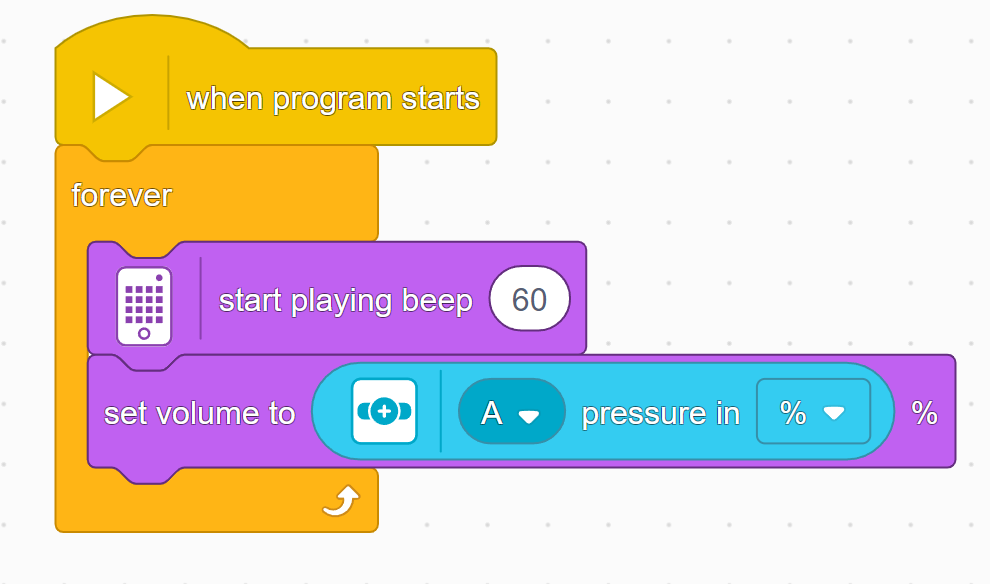
In this lesson, students will learn many of the key concepts needed for the rest of the course. That’s why there is little construction and mainly exploration with a single force sensor. Make sure they understand the difference between pitch and volume. Although there are many new blocks introduced, they are mostly simple and similar to previous ones. These blocks will also be used in many future lessons, giving students plenty of time to become familiar with them. By the end of the lesson, students should have tried the following two programs:
- #2502
- 16 Sep 2025