What Is a Hall Effect Sensor?
A Hall Effect Sensor is a small electronic component that detects magnets. When a magnet comes close, it sends a signal to other devices, like an Arduino or an LED light. Think of it as a tiny switch that turns on whenever a magnet is nearby.
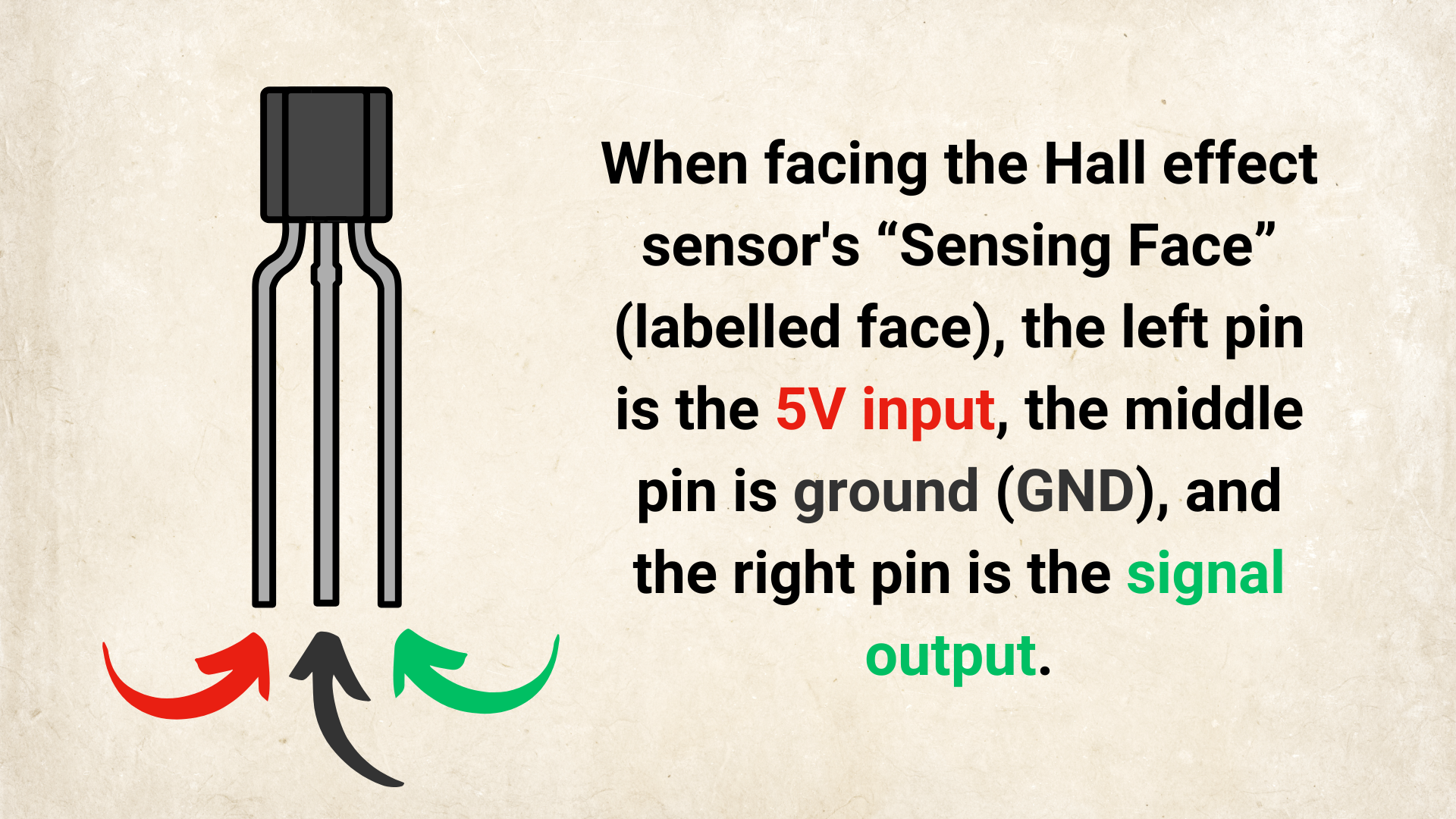
How Does It Work?
A Hall Effect Sensor has a tiny strip of conductive material inside. When current flows through it and a magnetic field is applied, a small voltage (the “Hall voltage”) appears and the chip turns that into a useful signal.
No magnet near the sensor → output stays at its normal level (for many digital sensors this is HIGH).
Magnet near the sensor → output changes (digital sensors usually go LOW; analog sensors shift up or down). Which pole (north/south) triggers it depends on the sensor’s orientation and type.
Applications of Hall Effect Sensors
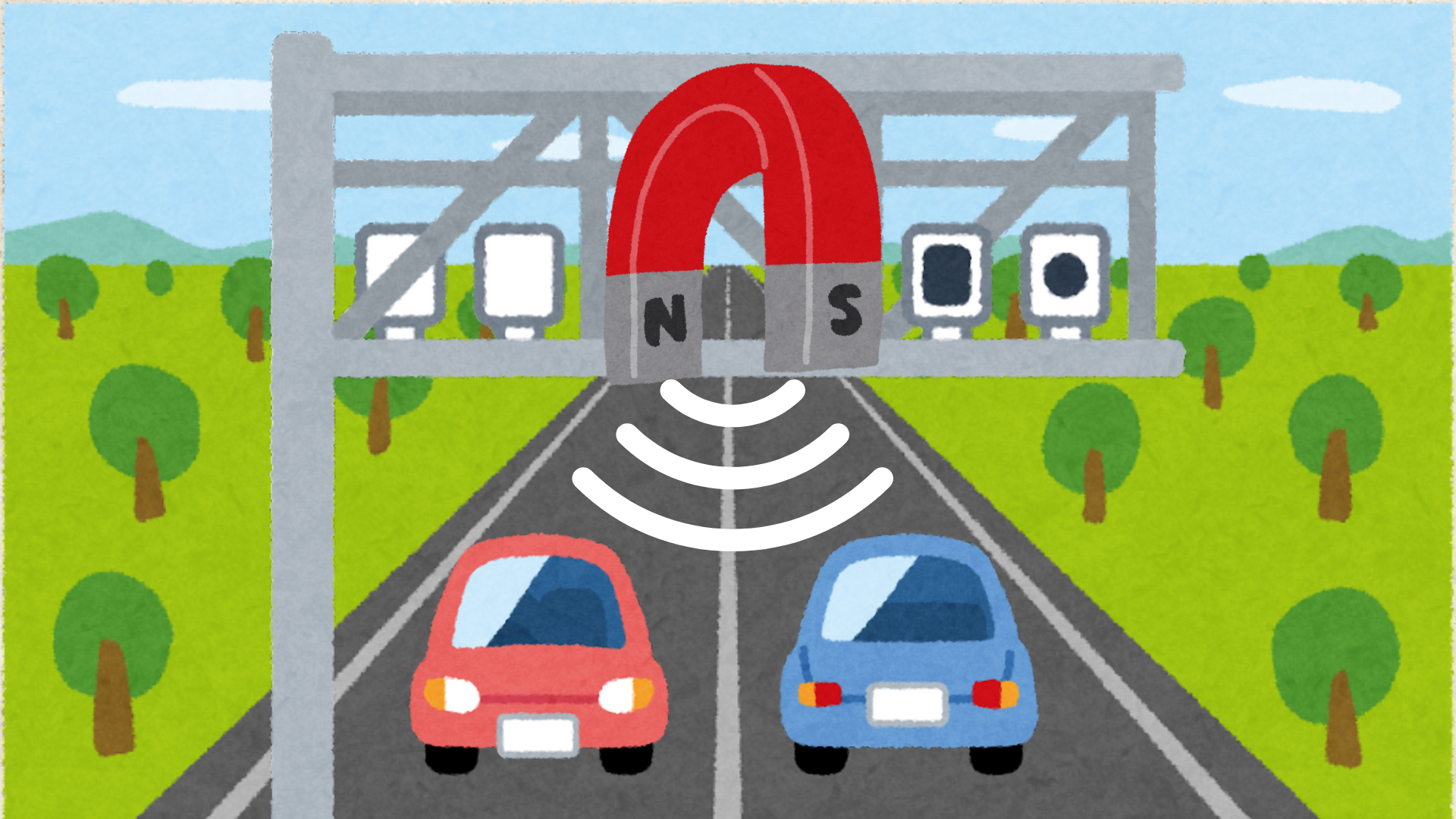
Automotive: Crankshaft/camshaft position, wheel speed (ABS), ignition timing.
Proximity: Detecting open/close in doors or lids.
Speed: Counting rotations in fans, motors, or wheels.
Current sensing: Measuring current without direct contact.
Position: Joysticks, gear shifters, and robotics.
Tips & Troubleshooting
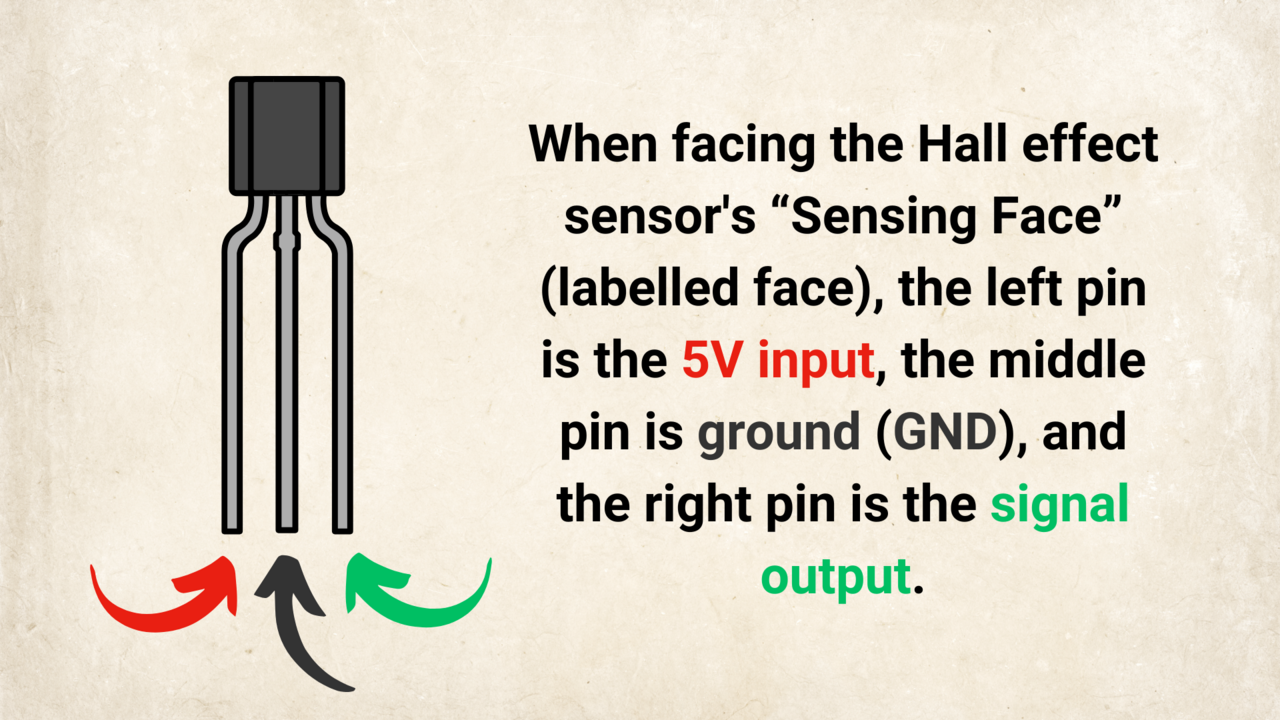
No output change? Check wiring (VCC, GND, OUT), flip the magnet, and adjust distance/strength.
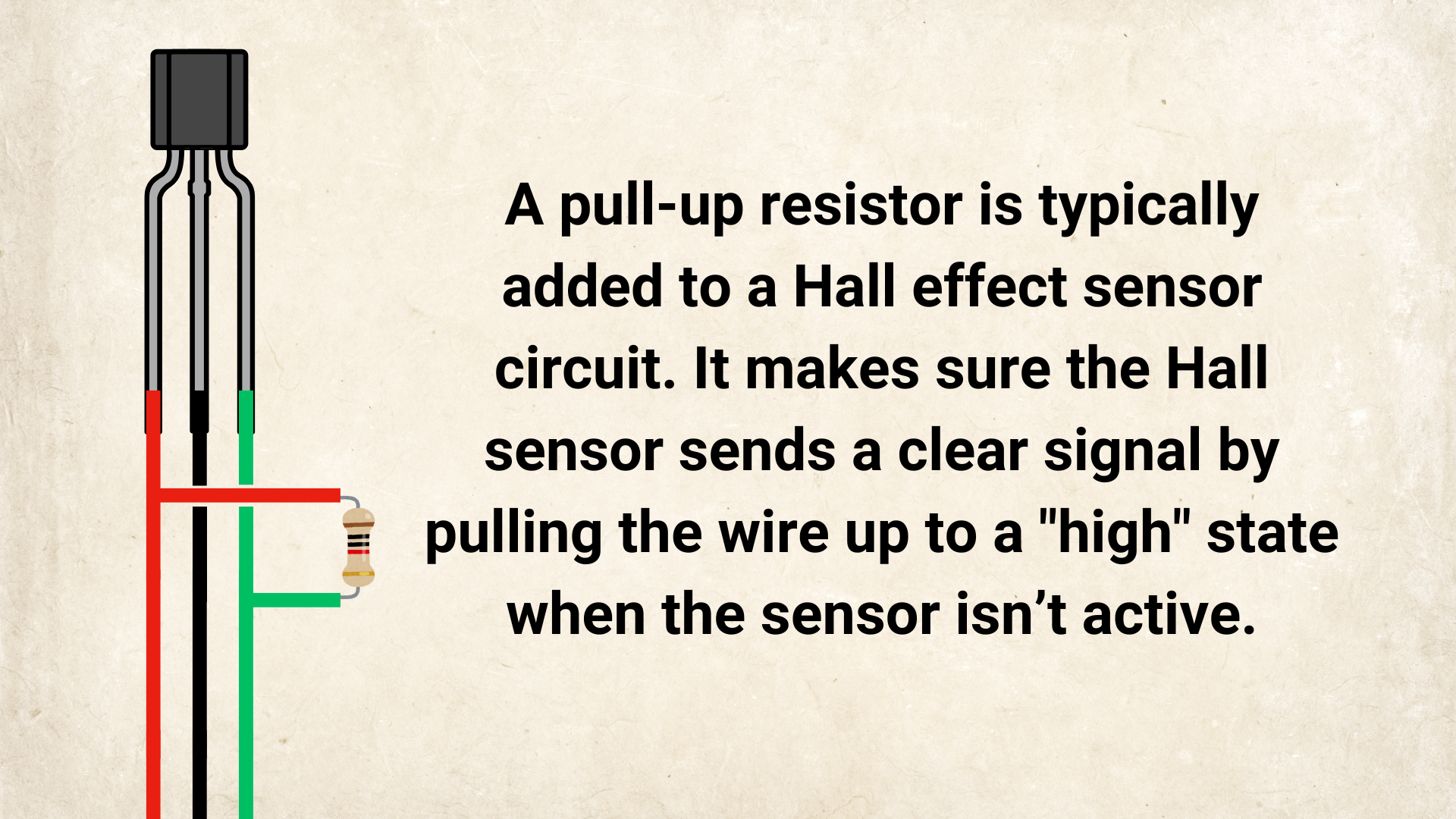
Digital output stuck HIGH? Many Hall sensors have an open-collector/open-drain output and need a pull-up resistor.
Using an analog Hall sensor? Read it with an ADC and consider smoothing (averaging) if the signal is noisy.