
Elevated places FIRST LEGO League 2019-2020 City Shaper Challenge
Move the robot to the bring. Bring the flags up
- #1422
- 21 Aug 2019

Move the robot to the bring. Bring the flags up


The goal of this lesson is to introduce students to the setting for measuring the reflected light of the color sensor and to recall how to follow a line.


Third wheel experiments, changes in the robot, students could choose the task all by themselves. Make sure you have a lot of fun and students complete their tasks. Here is what you should know when conducting this class.


The robot is equipped with two motors, one for each side. As a result, whenever the robot turns, it always follows an arc path. The size and radius of this arc can vary depending on the turn.


Here, we discuss the effects of applying this method to the two-state duck-following algorithm.


Before we can run our Python programs on the robot, we need to start the SPIKE software, create a Python project, and connect the Hub to the computer. In this tutorial, you will learn how to do all of these steps using the LEGO SPIKE software.


We have the following behavior expectations from you during this course:


Here’s a list of all the tools you’ll need to build the DIY Rotating LED Clock Display. Each tool links to Amazon. If a link isn’t available, we’ve included tips on how to find another one.


Here’s a list of all the parts you need to build the DIY Rotating LED Clock Display. Each part links to Amazon. If a link doesn’t work, don’t worry - we’ve also added tips on how to find a replacement.

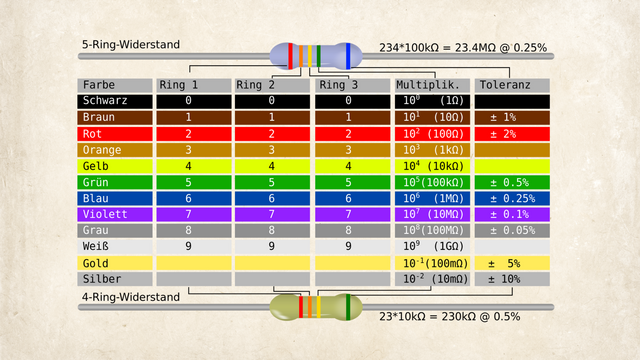

Resistors are essential electronic components that limit the flow of electric current in a circuit. Because they’re so small, their resistance value (measured in ohms, Ω) is usually marked with colored bands instead of numbers. Here's how to read them:
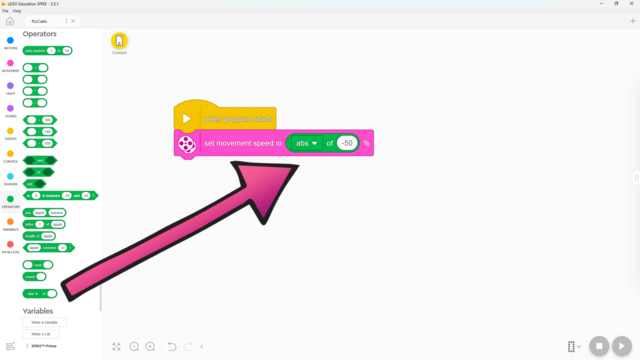

It is part of the Functions block, but what does it do?


Due to the long construction, you need to be careful with time in this lesson. Don’t let the students spend too much time building. If you think you can manage it, you may let them find their own sheet music and adapt it, but we recommend sticking to the short section from Ode to Joy as shown in the tutorial. This melody also serves as preparation for the next lesson, where a ready melody will again be needed. Here’s what the program looks like:
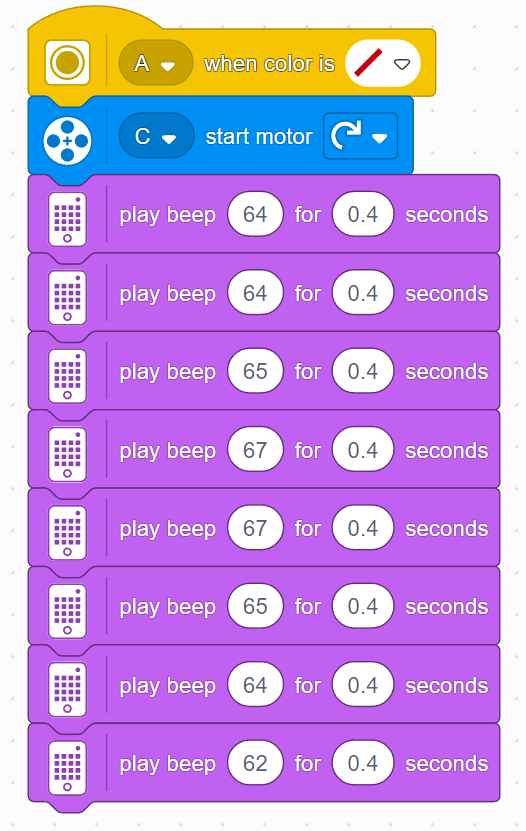


Because this is the musical level, it’s important to set some rules for the sounds the robots make. Students often don’t realize how loud it can get, so remind them to keep the volume lower so they can hear the hubs, and to stop their programs in time, since continuous sounds can become quite loud.
In this lesson, students will learn many of the key concepts needed for the rest of the course. That’s why there is little construction and mainly exploration with a single force sensor. Make sure they understand the difference between pitch and volume. Although there are many new blocks introduced, they are mostly simple and similar to previous ones. These blocks will also be used in many future lessons, giving students plenty of time to become familiar with them. By the end of the lesson, students should have tried the following two programs:
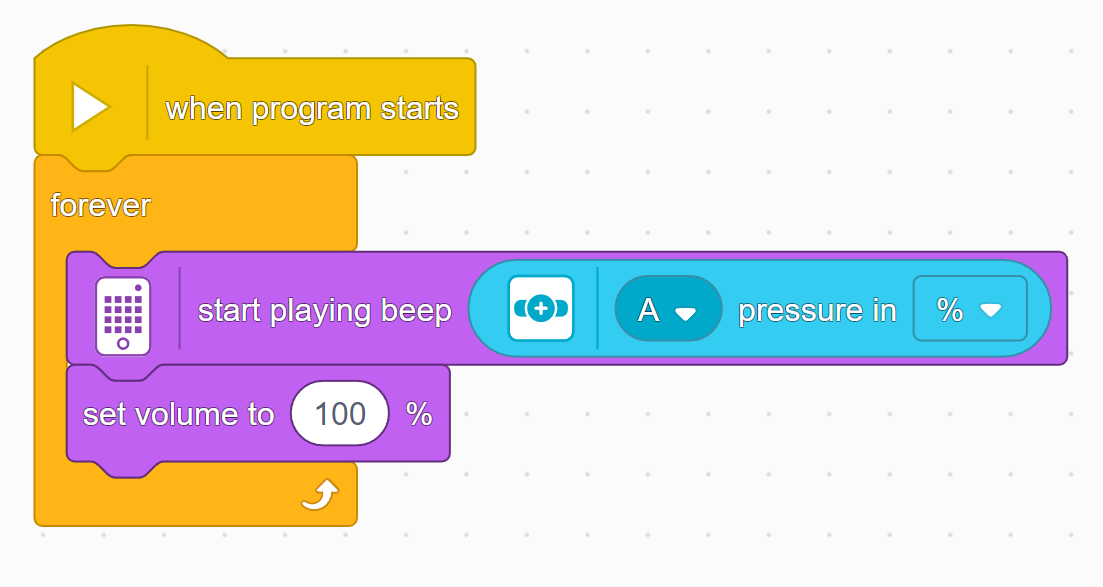
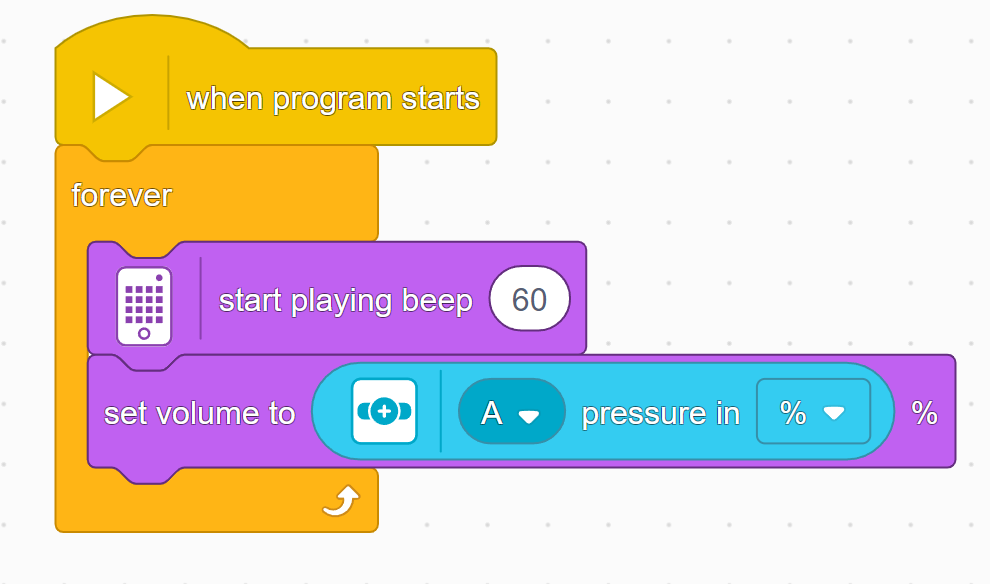
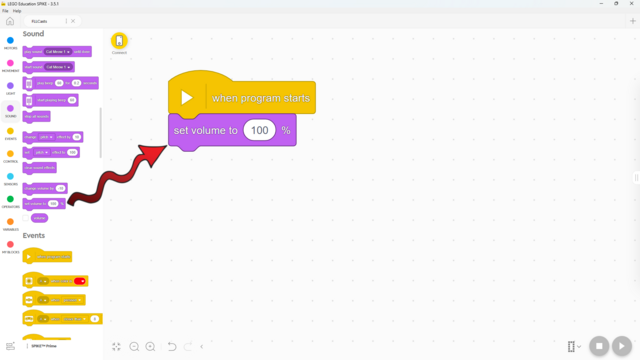

A big part of a sound is its volume. Here's how to change it!
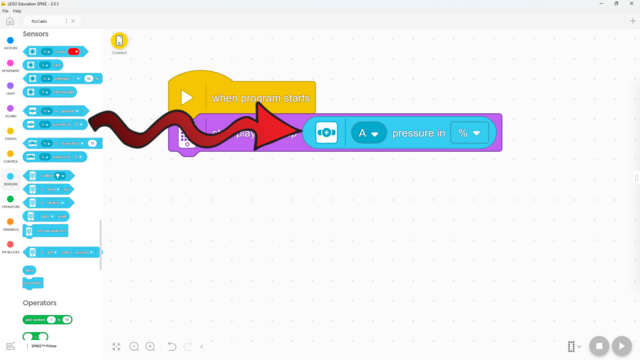

The force sensor can detect how hard it’s being pressed! Here’s how:
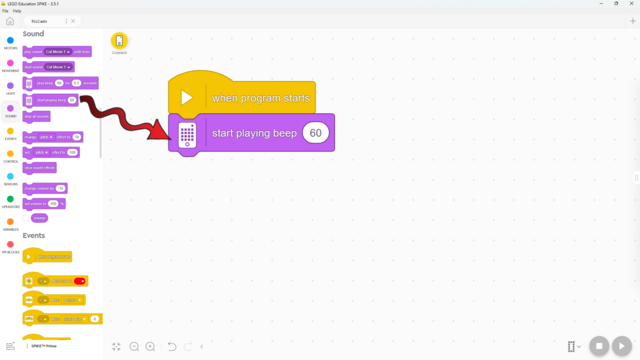

Did you know that your hub can play a sound? Here's how!