How to search for an unknown value with the fewest possible tries.
- #423
- 27 Apr 2017
- 6:27
The Problem
Often you will search for a motor rotation value in order to achieve some desired position of the robot. This process could take a lot of experiments and time if not approached structurally.
The approach - simple
Take a range of two values and make a test using their average. If the test is not satisfying, test again with a new range, based on the last test.
The algorithm
Phase one - find a value that is lower than the desired result and a value that is higher than the desired result.
Phase two - make a test using the average of the low and high values. In order to find the average, add the low to the high and divide the result by two.
Phase three - if the result is lower than the desired, change the initial lower value to the new average value and repeat phase two.
If the result is higher than the desired, change the initial high value to the new average value and repeat phase two.
Example
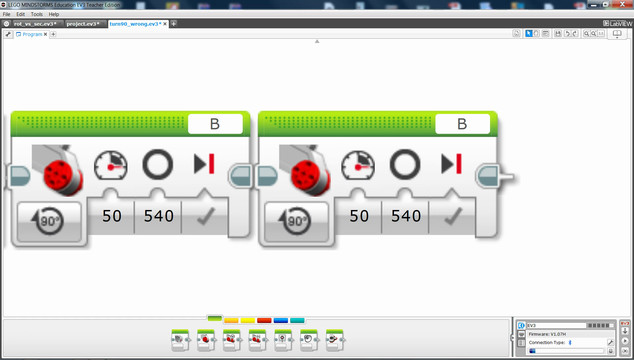
Find the value in degrees for a pivot turn to 90 degrees.
Step 1 (Phase one)
We measure that 360 is too low and 720 is too high.
Step 2 (Phase two)
The average value of the range from 360 to 720 is (360+720) / 2 = 540.
We test and see that 540 is too much.
Step 3 (Phase three)
Change 720 (initial high) to 540 degrees.
Step 4 (Phase two repeated with the new values)
The average value of the range from 360 to 540 is (360+540) / 2 = 450.
We test and see that 450 is too low.
Step 5 (Phase three repeated)
Change 360 (initial low) to 450 degrees.
Step 6 (Phase two repeated with new values)
The average value of the range from 450 to 540 is (450+540) / 2 = 495.
We test and see that 495 is good!
Comparison
It looks too long and difficult now.
But if we tried every 10 degrees, we would test 540, 530, 520, 510, 500 and 490 in order to find the value that we needed.
The direct approach testing every 10 degrees from 540 degrees downward takes 6 tests, whereas the binary search in the area from 360 to 720 degrees takes only three tests to find the correct value!
English
Turning with the wheel to 90 degrees does not result in turning the whole robot to 90 degrees. It's just the wheel. Again I'll set the wheel like this. The wheel turns to 90 degrees but not the whole robot. What we should do in this video is find the value for this construction for this wheel, for this robot of how much should we rotate the wheel so that the whole robot rotates to 90 degrees. In the software, I have the computer right beside me we have a program for turning this wheel to 360 degrees and I'll just start the program. 360 degrees with this wheel is not enough for turning the robot to the right - it's slightly to the right but not exactly to the right. What we can do is to experiment and to find the correct value. How do we find this value? There are many different ways. We can just try with 370 degrees or 380 degrees but that's kind of a slow process. What we can do is until we have the experience and you'll know most of the values by heart by the end of this course but for now what we can do is just double this value and set the value to 720 degrees. Like this.
So, 720 degrees is too much. We rotate the robot but not exactly to the right. It's to the right and then it continues forward. But what you can see is that 360 results in the robot positioned like this, 720 results in the robot positioned like this. So, it's somewhere in the middle and we can take the exact middle between 360 and 720. And the exact middle is 540. And if we set this to 540 degrees,
we see that it kind of looks like exactly to the right. Again.
But it's probably more. Exactly to the right would be like this. This process of finding the correct value is called Binary search. And it's very famous algorithm for seraching different values when we don't know them. And it's basically for searching in an array but these are details. With just 2 tries we find a value that's very close to the real one. How do we find if 540 degrees is the real one? What we should do is to make this robot turn to 540 degrees 4 times. And if it just rotates, then we know that the value of 540 is correct. How do we do this in the program?
We have our block - 540 and we must execute this block 4 times. Or even 10 times but 10 is too much. Let's start with 4. What we can do is we can take another block - Large block place it here then we can configure it for a number of degrees - for 540. But as you see this is kind of a slow process. What we can do is to copy. We can select this block, click edit > copy and then click edit > paste. And we have the same block here with the exact same configurations. But we can also do another trick. We can hold CTRL and move.
And this makes another copy of the same block and now we have 4 different blocks. And I'll just download and run these 4 different blocks.
The robot does 4 turns to 540 degrees. If each of these is exactly right then at the end it should arrive at the same position that it started. Because it will do a full circle. But as you saw 540 is a little too much.
At the end the robot is not facing exactly you on the camera and we use the marker, it moves slightly after the marker. So, the correct value is somewhere slightly less than 540 degrees. And we'll leave this to you. Try to find the correct value for making the whole robot turn to exactly 90 degrees and when you do 4 turns it should return to the same position.
Courses and lessons with this Tutorial
This Tutorial is used in the following courses and lessons
EV3 Phi. Introduction to robotics with LEGO Mindstorms
The things that you will be able to do with your EV3 robot by the end of this course are:
Freely move your robot towards desired target;
Avoid obstacles on the path of your robot using sensors;
Follow lines of any shape;
Detecting and picking up objects of any kind;
- 92
- 220:20
- 36

Turning with a LEGO Mindstorms Robot
So far we know how to make a turn in an arc, just like the real cars do.
Today we will see what other options our robots have for turning.
- 14
- 0
- 4
- 3d_rotation 0

Instructors Remote Training
If you are working with students and you want to introduce Robotics to your class or you want to mentor a FLL team, but you are insecure about your technical knowledge in the Robotics field, then this is the right place for you. Having in mind teachers' busy schedule, we have design two different schedules and added an option to design one just for you. FLLCasts's Mindstorms EV3 Robotics Online Training is the perfect match for any teacher.
After the completion of each task the participant has to upload his solution for verification.
- 183
- 280:11
- 156

How to make the robot move
Let's review the LEGO Mindstorms EV3 Intelligent Brick
The EV3 brick is the main computer of your LEGO robot and it has a display, a few buttons and various ports.
- 24
- 0
- 11
- 3d_rotation 0

Level B1. "Spy gadgets". Robotics with LEGO
The third level of the Robotics with LEGO curriculum for students in second, third or fourth grades.
In these lessons, we stress on more complex and challenging robots. The concept of Condition is introduced. Students learn about physics concepts of inertia and center of mass. Robots with two sensors are built and students program both of them. Programming becomes more complex as robots now can make complex decisions. "Spy"-robots sneakily follow their targets, trying to be undetected.
- 30
- 7:30
- 108
Robotics with LEGO - Level 1.0 - Adventure in Space
The first level of the Robotics with LEGO curriculum for students in fifth to twelfth grades.
Various constructions with robots are built. Learn how to control the motors so that the robot navigates around the Moon and Earth in various ways. Getting to know the first two sensors. The robot can feel its surroundings with the help of the Touch sensor and avoid obstacles.
The Ultrasonic distance sensor can help the robot avoid obstacles. Students work with concepts like loop, degrees and medium motor. Robots can now do two different actions at the same time - while solving missions on a field, the third motor clears detected obstacles.
- 126
- 123:52
- 150
Lesson 3 - Clearing the landing zone
Intro
Today we are building a robot, what would automatically clear the landing site.
Before a space craft lands on the moon, you send a robot to clear the landing site. Your robot has landed on the Moon and its task is to clear the site and to prepare it for the landing of the bigger space ship.
The robot lands slightly further away from the site and it must find its way to it. Regretably it road is blocked by rocks that can not be moved. The robot must go around them.

- 9
- 4
- 2
- 3d_rotation 0

Robotics with LEGO - Level 1.5 - Spy games
The second level of the Robotics with LEGO curriculum for students from fifth to twelfth grades.
Students build multiple robots with thread chains and become familiar with the physical concepts of momentum and center of gravity. The concept of gears, their use and basic constructions involving gears are studied.
The new concept of "condition" is introduced in programming. Robots are becoming smarter as they can make complex decisions on their own. "Spy robots" follow their targets and avoid being noticed. This level introduces the light sensor which the robots use to recognize the colors of the objects they are looking for. Robots can stop on a black line and follow a route marked with a colored line on the floor.
The spy's most complex mission in the end of the level is to turn into a sumo wrestler and defeat any other robot in the ring.
- 56
- 12:47
- 136

Level A1. Introduction. Robotics with LEGO
Introduction to robotics - The first level of the Robotics with LEGO curriculum for students in second, third or fourth grades. A journey in space, with robots. Various constructions with robots are built. Learn how to control the motors so that the robot navigates around the Sun, the Moon and Earth in various ways. Getting to know the first of the sensors. The robot can feel its surroundings with the help of the Touch sensor and avoid obstacles.
- 142
- 133:42
- 187
Lesson 5 - Clearing a landing spot
Remember to provide feedback to students regularly. It's important to give structured feedback in the form of a grade. Today, you'll need to grade your students following this article.
- 11
- 3
- 5
- 3d_rotation 0