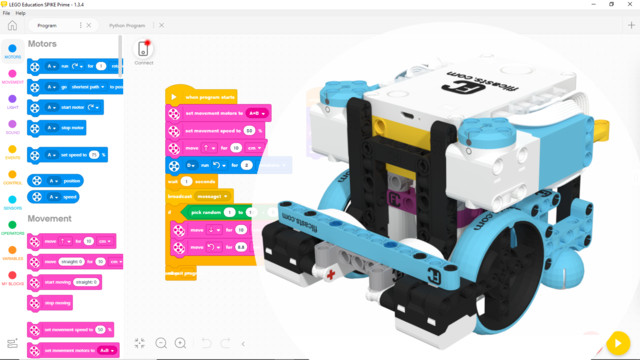
In this program we demonstrate how to program a SPIKE robot to execute a faster and more accurate turn. You can press the right button to see how the robot executes a 90-degree turn with the aid of acceleration, to improve accuracy. After that, you can press the left button to see the robot turn fast with to acceleration, overshoot the target angle, and then return slowly back to it. That way, the robot reaches the target angle faster and more accurately. This method is useful for larger turns when time is limited. For smaller turns, it may cause the opposite effect. Since the robot, this program was made for, is a little tilted, the angle it is programmed to turn to is changed a little to compensate for the tilt.
This program was intended for and tested on the Gazon robot